Third-party cyber risk management (TPCRM & TPRM) has become a critical focus for businesses due to the rising prevalence of supply chain attacks. Attackers have increasingly shifted their techniques, exploiting opportunities to spread their attacks through third-party entities, making risk management essential for safeguarding organizational security. For example, the 2023 MOVEit breach began when attackers exploited a vulnerability in the MOVEit file transfer software used by numerous organizations, allowing unauthorized access to sensitive customer and organizational data and resulting in widespread data exposure and significant financial and reputational damage.
Managing these risks involves identifying vulnerabilities, monitoring vendor security practices, and addressing potential threats before they escalate. In this article, we’ll explore the fundamentals of third-party cyber risk management, highlight the types of risks businesses face, and discuss why every industry must adopt a proactive approach to secure their vendor ecosystem.
What is Third Party Cyber Risk Management?
Third-party cyber risk management is the practice of identifying, monitoring, and mitigating cybersecurity risks introduced by external vendors, suppliers, or service providers. These third parties often have access to critical systems, proprietary data, and sensitive customer information, making them a potential gateway for cyber threats.
For example, many organizations use third-party cloud storage providers to handle sensitive data. If the provider’s security protocols are weak, a data breach could compromise not only their systems but also the businesses they serve. Similarly, outsourcing IT support may streamline operations, but it can also introduce risks if those vendors fail to implement proper security measures.
The goal of third-party cyber risk management is to proactively address these risks before they escalate into costly incidents. This involves evaluating the cybersecurity practices of third parties, ensuring compliance with relevant standards, and establishing clear incident response protocols. Without this level of scrutiny, businesses are effectively gambling with their own security.
Key Functions of TPCRM
- Risk Assessment: Evaluating the potential impact and likelihood of third-party vulnerabilities.
- Continuous Monitoring: Keeping tabs on vendor security practices to detect emerging risks.
- Vendor Agreements: Establishing security requirements in contracts to set expectations.
- Remediation Plan: Guidance with step-by-step instructions, prioritization of actions, strategies for mitigation, and detailed approaches to addressing identified risks and issues.
Understanding and implementing third-party cyber risk management isn’t just good practice—it’s a business imperative.
Types of Cyber Risks in Third-Party Relationships
Businesses face numerous cyber risks when working with third-party vendors, often because these external partners don’t always share the same rigorous security standards. Understanding these risks is the first step in mitigating them. Below are the most common types of cyber risks associated with third-party relationships:
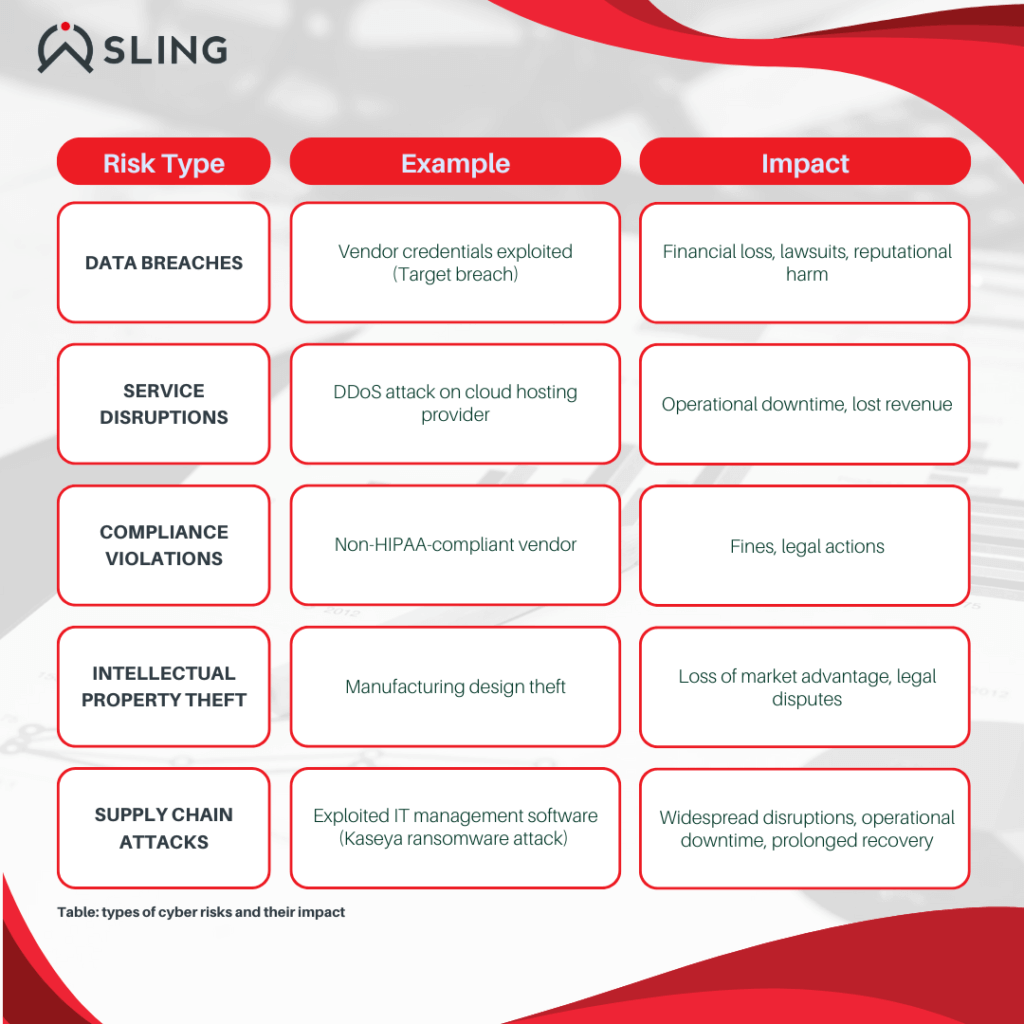
1. Data Breaches
Third parties often handle sensitive customer, employee, or company data. If a vendor’s security systems are compromised, attackers can exploit their access to infiltrate your network.
- Example: In the Target breach mentioned earlier, hackers accessed Target’s payment system through a vendor’s compromised credentials, exposing millions of customer records.
- Impact: Financial losses, legal liability, and reputational damage.
2. Service Disruptions
If a vendor falls victim to a cyberattack, their systems could be rendered inoperable, impacting your operations.
- Example: A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack on a cloud hosting provider could shut down critical systems for hours or even days.
- Impact: Lost productivity, missed revenue, and damage to customer trust.
3. Compliance Violations
Regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, DORA and NIS2 hold businesses accountable for protecting data, even if it’s managed by third parties.
- Example: A healthcare provider using a vendor that doesn’t comply with HIPAA could face steep fines if patient data is compromised.
- Impact: Regulatory penalties and increased scrutiny from auditors.
4. Intellectual Property Theft
Third parties with access to proprietary information, like product designs or trade secrets, can inadvertently expose it through weak security measures.
- Example: A manufacturing company’s design files could be stolen through a compromised vendor network, leading to counterfeit products in the market.
- Impact: Loss of competitive advantage and potential legal disputes.
5. Supply Chain Attacks
Cybercriminals often target vendors to infiltrate their clients’ systems, leveraging the trust between the two parties.
- Example: In 2021, the Kaseya ransomware attack targeted a widely used IT management software vendor. Attackers exploited vulnerabilities in the vendor’s system to deploy ransomware to hundreds of the vendor’s clients, affecting businesses globally, including schools, hospitals, and retail chains.
- Impact: Widespread operational disruptions, financial losses from ransom payments, and significant downtime for affected organizations.
Sling’s Solution for Third-Party Cyber Risk Management
Managing third-party cyber risks effectively requires sophisticated tools and a proactive approach. Sling offers a comprehensive solution tailored to the complexities of modern vendor networks, providing organizations with the tools they need to stay ahead of threats.
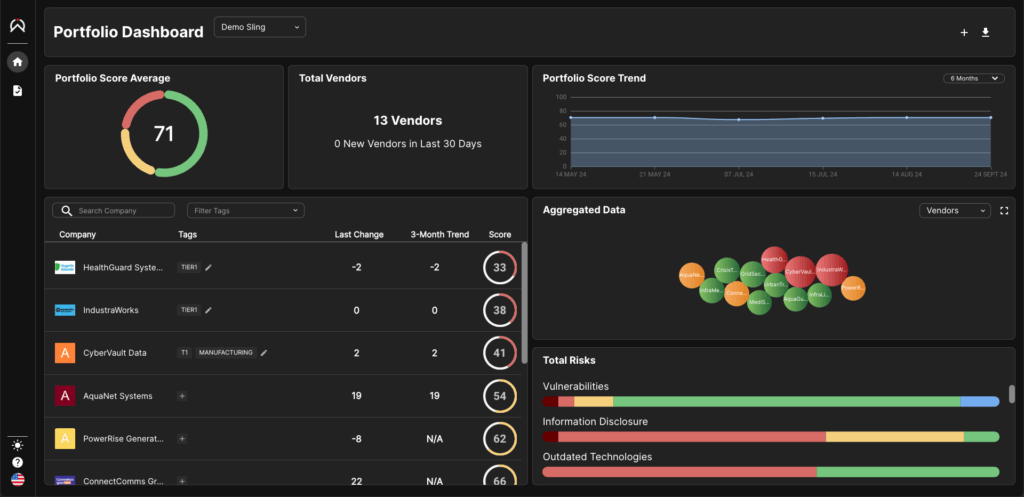
1. Proprietary Risk Scoring
Sling’s platform uses advanced algorithms to calculate a unique sling score for each third party, combining multiple data points to create a comprehensive risk profile.
- Key Inputs:
- Comprehensive and detailed reports on risks associated to the overall portfolio components and the specific risks introduced by each company, featuring a prioritized analysis of critical issues.
- Analysis of asset vulnerabilities.
- Findings from Darknet data regarding potential attacks.
- Benefit: Organizations gain a clear understanding of their most vulnerable third-party relationships and can prioritize remediation efforts accordingly.
2. Continuous Monitoring
Sling provides real-time visibility into the security practices of third-party vendors, ensuring that any emerging risks are detected early.
- Features:
- Automated alerts for risk issues or non-compliance issues.
- Regular updates on vendor security postures.
- Integration with existing incident management workflows.
- Benefit: Businesses can take immediate action to mitigate risks before they escalate into incidents.
3. Attacker’s View
Sling integrates threat intelligence that simulates how attackers view and prioritize vendor vulnerabilities. By understanding the attacker’s tactics, Sling helps organizations strengthen their defenses where it matters most.
- Features:
- Identification of high-value vendor targets based on their access levels and vulnerabilities.
- Insights into the attack surface exposed by third-party connections.
- Benefit: Organizations gain an understanding of where attackers are most likely to strike and can take preventive measures.
4. Actionable Insights and Tailored Reporting
Sling delivers detailed, actionable reports designed to help businesses strengthen their cybersecurity strategies. These reports include practical recommendations tailored to each vendor’s risk profile.
- Example Reports:
- Portfolio Report: provides an in-depth view of your vendors’ overall security posture, highlighting key insights into how their risk profiles and scores shape your portfolio’s cyber resilience.
- Cyber Risk Report: delivers a detailed analysis of a specific vendor’s cybersecurity posture, highlighting the risks contributing to their Sling Score.
- Benefit: Companies are empowered to make data-driven decisions to protect their operations.
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
| Proprietary Risk Scoring | Combines intelligence, vulnerabilities, and Darknet data | Identifies high-risk vendors |
| Continuous Monitoring | Real-time tracking of vendor security | Early detection of emerging risks |
| Attackers View | Graphic view of attackers perspective on vulnerabilities | Allows to take preventative measures before attackers strike |
| Actionable Insights | Tailored reports with practical recommendations | Data-driven cybersecurity decisions |
How to Get Started with Third-Party Cyber Risk Management
Managing third-party cyber risks can seem complex, but with the right tools and strategies, you can safeguard your business from vulnerabilities introduced by external vendors. By conducting risk assessments, setting clear security standards, monitoring vendor activities, and preparing for incidents, you’re laying the groundwork for a strong cybersecurity posture.
However, implementing these steps effectively requires the right platform and expertise. That’s where Sling’s third-party risk management solution comes in. With advanced technologies like Sling, you can take full control of your vendor ecosystem, proactively identify vulnerabilities, and mitigate risks before they escalate.
Ready to protect your business and secure your supply chain?
Book a personalized demo today to see how Sling can transform your third-party risk management strategy. Learn how to assess your vendors, monitor threats in real time, and build a proactive incident response plan—all in one comprehensive platform.
Schedule Your Demo Now
Let Sling help you secure your business beyond borders. Don’t wait—start mitigating your risks today!



