Cybersecurity is a critical concern in the current digital ecosystem, with businesses facing ever-growing threats to their data and operations. The choice between reactive and proactive cybersecurity measures can make the difference between resilience and vulnerability. Reactive strategies focus on responding to incidents after they occur, often leading to significant damage control efforts. On the other hand, proactive approaches aim to prevent threats before they materialize, offering organizations a way to stay ahead of cyber risks.
By comparing these two approaches, it becomes evident that adopting a preventive mindset is not just a recommendation but a necessity. Understanding how these strategies align with business goals and exploring tools like Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) and risk scoring can help organizations protect their data, reputation, and bottom line.
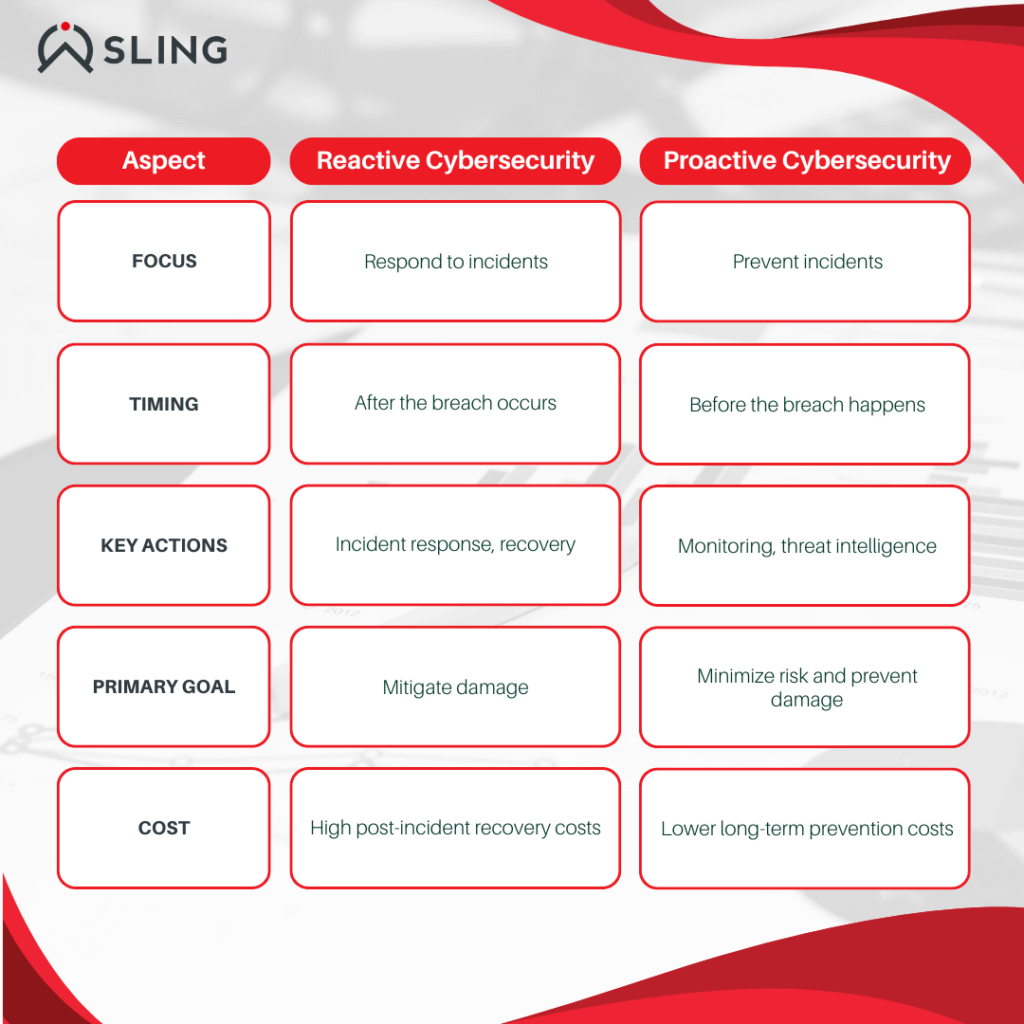
Proactive vs Reactive Cybersecurity: A Fundamental Difference
What is Reactive Cybersecurity?
Reactive cybersecurity is the process of addressing and mitigating cyber threats after they have already occurred. This approach includes actions such as:
- Incident response plans
- Forensic analysis to determine the scope of an attack
- Disaster recovery procedures
While reactive measures are essential for damage control, they often come at a high cost. The time between a breach and response can lead to significant data loss, financial repercussions, and damage to an organization’s reputation.
What is Proactive Cybersecurity?
Proactive cybersecurity involves anticipating, detecting, and neutralizing threats before they materialize. Key components of a proactive approach include:
- Continuous network monitoring
- Implementation of advanced threat detection tools
- Regular vulnerability mitigation
By taking a preventive stance, organizations can minimize potential damage and ensure business continuity. Proactive cybersecurity also strengthens trust and enhances compliance with evolving regulatory requirements.
The Downsides of a Reactive Approach
Financial Costs
Reactive cybersecurity often results in significant financial costs. The average global cost of a data breach has risen to $4.88 million. Organizations incur expenses on containment, legal fees, and recovery efforts, while downtime during recovery leads to further losses in revenue and productivity.
Reputational Damage
Data breaches erode customer trust and can damage a company’s brand for years. According to a Forbes survey, 46% of customers stop doing business with companies that have experienced a breach. Rebuilding trust often requires extensive investments in public relations and customer outreach.
Regulatory and Compliance Risks
Failing to prevent cyber incidents can result in severe regulatory penalties. For example, the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) imposes fines of up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover for non-compliance. A reactive approach makes it harder to meet these requirements and avoid penalties.
Why Proactive Cybersecurity is the Future
Early Threat Detection
Proactive measures allow organizations to identify and neutralize threats before they escalate. Tools like Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) and cyber risk scoring provide real-time insights into potential vulnerabilities and help prioritize preventive actions.
Enhanced Compliance
Proactive strategies align with regulatory requirements by ensuring consistent monitoring, reporting, and documentation. This reduces the risk of fines and legal action.
Cost Efficiency
Prevention is always cheaper than cure. Investing in preventive measures saves organizations from the steep costs of post-incident recovery, legal fees, and regulatory fines.
Transitioning to Proactive Cybersecurity
Shifting to proactive cybersecurity requires a focus on prevention and continuous monitoring. Key actions include:
- Identify critical assets: Determine which systems, data, and processes are most important to your organization’s operations.
- Evaluate access controls: Ensure appropriate permissions are in place to limit access to sensitive information.
- Conduct regular risk assessments and leverage TPRM tools: Uncover vulnerabilities in internal systems and third-party relationships, while using Third-Party Risk Management tools for:
- Ongoing monitoring of third-party activities
- Real-time alerts for emerging vulnerabilities
- Actionable insights through dashboards and analytics
Proactive cybersecurity is no longer optional in a world where threats grow more sophisticated by the day. While reactive measures remain necessary for addressing incidents, the real value lies in preventing breaches before they happen. By identifying critical assets, conducting regular risk assessments, and leveraging tools like Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) and risk scoring, organizations can stay ahead of potential threats.
This approach not only reduces vulnerabilities but also strengthens overall security, protects sensitive data, and maintains the trust of stakeholders. In today’s interconnected landscape, embracing a proactive mindset is essential for long-term success and resilience in the face of ever-evolving cyber challenges.



